- EFFICACY
- PFS in GEP-NETs
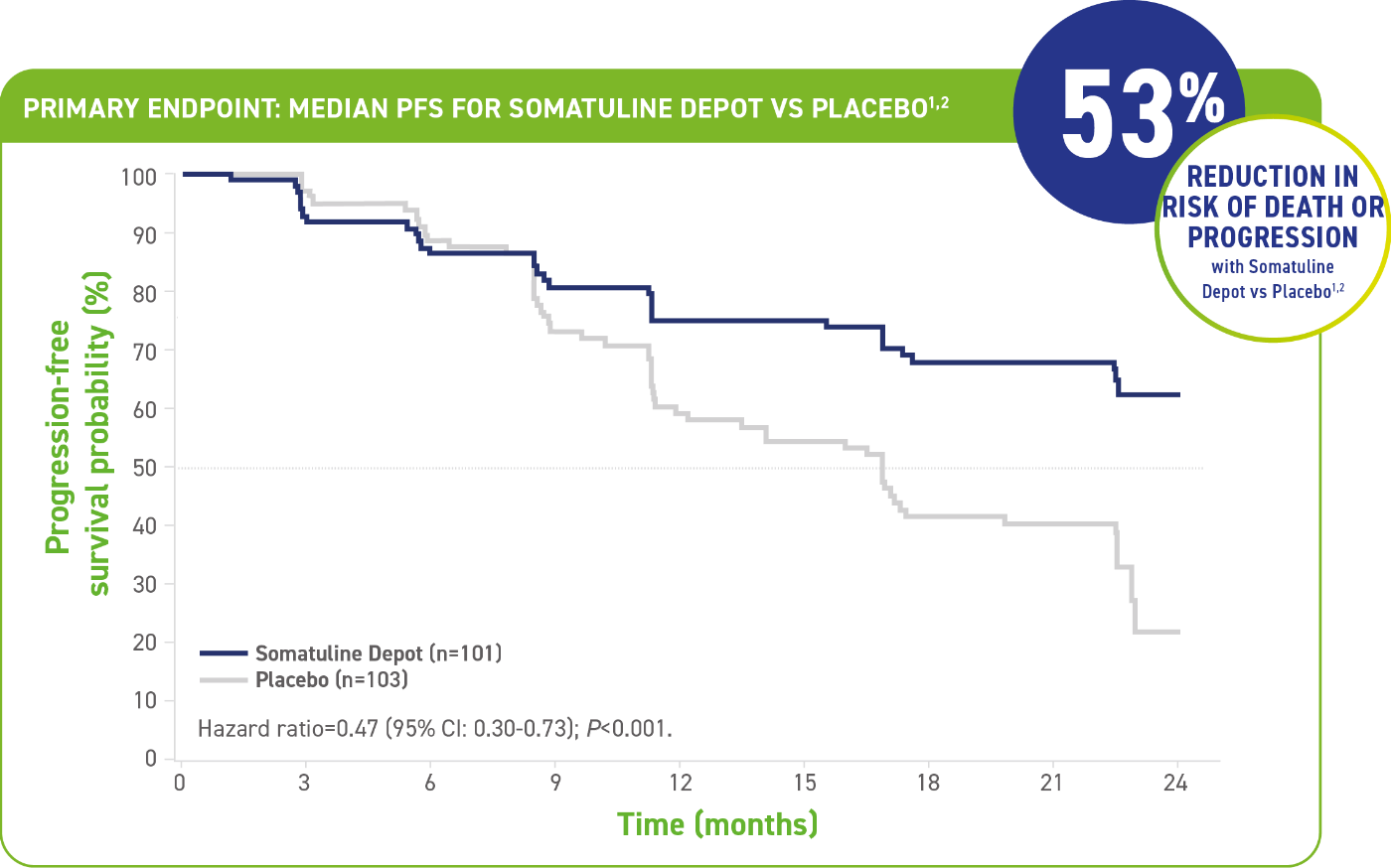
PROVEN FOR PFS IN PATIENTS WITH GEP-NETs1,2
Somatuline® Depot reduced the risk of tumor progression by greater than half vs placebo1,2
Somatuline Depot improved PFS for patients with GEP-NETs – studied in adult patients with unresectable, well- or moderately-differentiated, locally advanced or metastatic
GEP-NETs1,2
- The median PFS for Somatuline Depot was not yet reached at 22 months (95% CI: NE, NE) compared with 16.6 months for placebo (95% CI: 11.2-22.1)1
- Number of events (N=204): Somatuline Depot 32 (31.7%) vs placebo 60 (58.3%)1
CI=confidence interval; FDA=Food and drug Administration;
GEP-NET=gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; NE=not estimable;
PFS=progression-free survival.
NE=Not reached at 22 months.1
An FDA-approved treatment in GEP-NETs proven to reduce tumor growth1,2
- The median PFS for Somatuline Depot was not yet reached at 22 months (95% CI: NE, NE) compared with 16.6 months for placebo (95% CI: 11.2-22.1)1
- Number of events (N=204): Somatuline Depot 32 (31.7%) vs placebo 60 (58.3%)1
CI=confidence interval; FDA=Food and drug Administration;
GEP-NET=gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; NE=not estimable; PFS=progression-free survival.
NE=Not reached at 22 months.1

Adverse reactions reported in the CLARINET study1
Most common adverse reactions (greater than 10%) were abdominal pain, musculoskeletal pain, vomiting, headache, injection site reaction, hyperglycemia, hypertension, and cholelithiasis.1
Please also see CLARINET trial study design and Patient Information below.
Please also see CLARINET trial study design and Patient Information below.
Study design and patient population information
CLARINET: A Phase 3 trial of an SSA powered for PFS and one of the largest studies of the antitumor effect in patients with GEP-NETs1,2
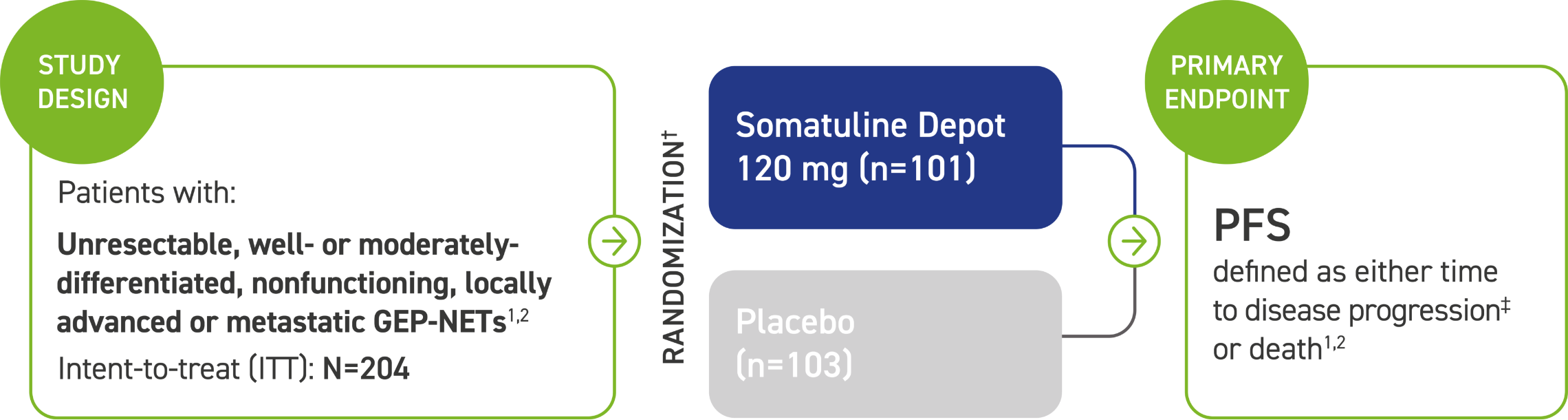
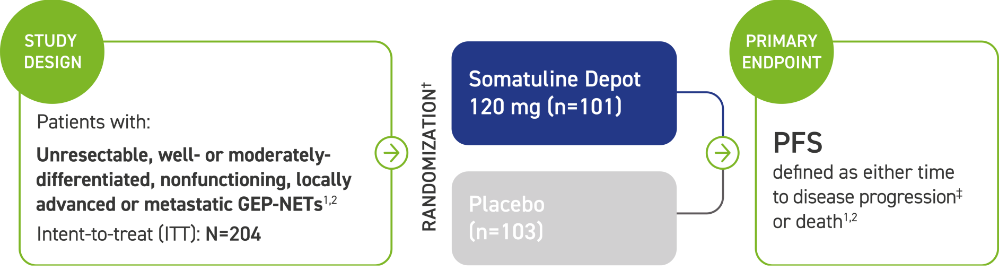
The majority (84%) of patients in CLARINET had not received prior pharmacologic therapy for GEP-NETs. Some patients (16%) received prior therapy.2
Patients were excluded if they received:2
- An SSA at any time, unless they received it >6 months prior to study entry and for <15 days
- Interferon, chemoembolization, or chemotherapy: <6 months prior to study entry
*CLARINET=Controlled Study of Lanreotide Antiproliferative Response In NeuroEndocrine Tumors.2
†Administered every 28 days by deep subcutaneous injection. Follow-up visits occurred at Weeks 12, 24, 36, 48, 72, 96.2
‡Assessed by a central independent radiological review in accordance with the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.0.1,2
Disease characteristics
Progression-free survival studied in a comprehensive and robust patient population2
CLARINET trial included patients with unresectable, well- to moderately differentiated, locally advanced or metastatic GEP-NETs, a range of hepatic tumor loads, and varying primary tumor locations (pancreas, midgut, or hindgut).2
Main characteristics and treatment options from patients included in the Phase 3 trials evaluating the role of SSAs in NETs1-3
|
Localization |
Midgut |
Pancreas |
High liver tumor burden (>25%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grade of Differentiation |
G1 |
G2 |
G1 |
G2 |
||
|
Ki-67 |
<2% |
2%-10% |
<2% |
2%-10% |
||
|
First-Line SSA |
Somatuline |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Localization |
Midgut |
Pancreas |
High liver tumor burden(>25%) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grade of Differentiation |
G1 |
G2 |
G1 |
G2 |
|
|
Ki-67 |
<2% |
2%-10% |
<2% |
2%-10% |
|
|
First-Line SSA Treatment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Somatuline Depot* |
|||||
Adapted from Pozas J, San Román M, Alonso-Gordoa T, et al. Targeting angiogenesis in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: resistance mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4949.
*Baseline prognostic characteristics were similar between arms with one exception: There were 39% of patients in the Somatuline Depot arm and 27% of patients in the placebo arm who had hepatic involvement by tumor of >25%.1
FDA=Food and Drug Administration; G=grade; GEP-NET=gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; ITT=intent-to-treat; PFS=progression-free survival; SSA=somatostatin analog.
REFERENCES:
- Somatuline Depot (lanreotide) Injection [Prescribing Information]. Cambridge, MA: Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Inc.; July 2024.
- Caplin ME, Pavel M, Ćwikła JB, et al.; on behalf of the CLARINET Investigators. Lanreotide in metastatic enteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(3):224-233.
- Pozas J, San Román M, Alonso-Gordoa T, et al. Targeting angiogenesis in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: resistance mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4949.


